Abstract
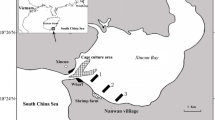
Porewater nutrient profiles such as nitrate (0.33–1.38 μM), ortho phosphate (1.47–3.44 μM), total nitrogen (1.24–7.22 μM) and total phosphorus (3.51–5.98 μM) in seagrass ecosystem subjected to different nutrient loading indicated the limitation of porewater nutrients in all the strata of different sampling sites of Palk Bay region. Sediment pH in the seagrass beds were alkaline and anoxic condition increased with increase in depth (56.2 mV to −52.7 mV). Significant positive correlation was observed between silt content and carbon (r = 0.359, P < 0.05) and nitrogen contents (r = 0.381, P < 0.05) of the sediment. Specieswise interpretation also indicated C/N ratio of the stations greatly promoted the biomass in Halodule pinifolia and Cymodocea serrulata. The sediment C/N stoichiometry (4.7: 1–16: 1) indicated that autochthonous C sources regulates the C biogeochemical processes in seagrass ecosystem which is well corroborated by the least square regression value (R 2 = 0.92) obtained between the C/N ratio and biomass. Meanwhile, the N/P ratio (11.7: 1–17.2: 1) indicated P deficiency in the seagrass beds. Though, nitrogen limitation was evident in the porewater, but it has not reflected on seagrass biomass and productivity which is, evidenced by the higher biomass of individual species. Nutrient biogeochemical transformations across the sediment-water interface influence the productivity of seagrasses in the Palk Bay region. In addition, nutrient pollution, eutrophication and light limitation due to algal mats decreased the growth of seagrasses which need to be attempted to develop the nutrient policies for sustainable management and restoration of seagrass ecosystem.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
G. L. Chmura, S. C. Anisfeld, D. R. Cahoon, and J. C. Lynch, “Global carbon sequestration in tidal, saline wetland soils,” Global Biogeochem. Cycles 17, 1111 (2003).
P. M. Eldridge and M. G. Johnson, “Seagrass-sediment interactions,” in US Environmental Protection Agency, Washington DC, 2004), pp. 1–14.
S. Entriquez, N. Marba, C. M. Duarte, B. I. van Tussenbroek, and G. Reyes-Zavala, “Effects of seagrass Thalassia testudinum on sediment redox,” Mar. Ecol.: Progr. Ser. 219, 149–158 (2001).
P. C. A. Erftemeijer and J. J. Middelburg, “Sediment nutrient interactions in tropical seagrass beds: a comparison between a terrigenous and a carbonate sedimentary environment in South Sulawesi (Indonesia),” Mar. Ecol.: Progr. Ser. 102, 187–198 (1993).
P. L. A. Erftemeijer and J. J. Middelburg, “Mass balance constraints on nutrient cycling in tropical seagrass beds,” Aquat. Bot. 50, 21–36 (1995).
E. Gacia, and C. M. Duarte, “An approach to the measurement of particle flux and sediment retention within seagrass (Posidonia oceanic) meadows,” Aquat. Bot. 65, 255–268 (2001).
A. B. Hebert, Diagenesis in Seagrass Vegetated Sediments: Biogeochemical Processes On Diurnal Time Scales, Ph.D Thesis, (Texas A & M University, 2004).
F. M. L. Heijs, Some structural and functional aspects of the epiphytic component of four seagrass species (Cymodoceoidae). Aquat. Bot. 23, 225–247 (1985).
M. A. Hemminga and C. M. Duarte, Seagrass Ecology (Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, 2000).
M. A. Hemminga, P. G. Harrison, and F. van Lent, “The balance of nutrient losses and gains in seagrass meadows,” Mar. Ecol.: Progr. Ser. 71, 85–96. (1991).
M. Holmer, and S. L. Nielson, “Sediment sulfur dynamic related to biomass-density patterns in Zostera marina (eelgrass) beds,” Mar. Ecol.: Progr. Ser. 46, 163–171 (1997).
M. Holmer, “Productivity and biogeochemical cycle in seagrass ecosystems,” in Coastal Wetlands: an Integrated Ecosystem Approach, Ed. by G. M. R. Perillo, E. Wolanski, D. R. Cahoon, and M. M. Brinson (Elsevier Science, Amsterdam, 2009), pp. 377–402.
M. Holmer, F. O. Andersen, S. L. Nielsen, and T. S. Boschker-Henricus, “The importance of mineralization based on sulfate reduction for nutrient regeneration in tropical seagrass sediments,” Aquat. Bot. 71, 1–17 (2001).
R. W. Howarth, H. J. Jensen, R. Marino, and H. Postma, “Transport to and processing of P in nearshore and oceanic waters,” in SCOPE 54, Phosphorus in the Global Environment. Transfers, Cycles, and Management, Ed. by H. Thiessen (John Wiley and Sons, New York, 1995), pp. 323–345.
R. A. Jahnke, “A simple, reliable, and inexpensive pore-water sampler,” Limnol. Oceanogr. 33, 483–487. 1988.
J. E. Kaldy, “Production ecology of the non-indigenous seagrass, dwarf eelgrass (Zostera japonica Ascher. & Graeb.), in a Pacific northwest estuary, USA,” Hydrobiologia 553, 201–217 (2006).
L. Kannan, and T. Thangaradjou, “Identification and assessment of biomass and productivity of seagrasses,” in National Training Workshop on Marine and Coastal Biodiversity Assessment for Conservation and Sustainable Utilization (SDMRI Publication, 2006), pp. 9–15.
L. Kannan, and T. Thangaradjou, “Seagrasses,” in Biodiversity in Mangrove Ecosystem, UNU-UNESCO International Training Course, Course Manual, 130–136 (2003).
H. Kennedy, E. Gacia, D. P. Kennedy, S. Papadimitriou, and C. M. Duarte, “Organic carbon sources to SE Asian coastal sediments,” Estuarine, Coastal Shelf Sci. 60, 59–68 (2004).
W. J. Kenworthy and M. S. Fonseca, “The use of fertilizer to enhance growth of transplanted seagrasses Zostera marina L. and Halodule wrightii Aschers,” J. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 163, 141–161 (1992).
M. S. Koch, S. A. Schopmeyer, C. Kyhn-Hausen, C. J. Madden, and J. S. Peters, “Tropical seagrass species tolerance to hypersalinity stress,” Aquat. Bot. 86, 14–24 (2007).
E. Kristensen, M. H. Jensen, G. T. Banta, K. Hansen, M. Holmer, and G. M. King, “Transformation and transport of inorganic nitrogen in sediments of a Southeast Asian mangrove forest,” Aquat. Microbial Ecol. 15, 165–175 (1998).
K. S. Lee, and K. H. Dunton, “Effects of nitrogen enrichment on biomass allocation, growth, and leaf morphology of the seagrass Thalassia testudinum,” Mar. Ecol. 196, 39–48 (2000).
K. S. Lee, S. R. Park, and J. B. Kim, “Production dynamics of the eelgrass, Zostera marina in two bay systems on the south coast of the Korean peninsula,” Mar. Biol. 147, 1091–1108 (2005).
R. Lindholm, A Practical Approach to Sedimentology (Allen and Unwin, London, 1987).
M. L. Cambridge and G. A. Kendrick, “Contrasting responses of seagrass transplants (Posidonia australis) to nitrogen, phosphorus and iron addition in an estuary and a coastal embayment,” J. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 371, 34–41 (2009).
N. Marba, M. Holmer, E. Gacia, and C. Barron, “Seagrass beds and coastal biogeochemistry,” in Seagrasses: Biology, Ecology and Conservation, Ed. by A.W.D. Larkum, R. J. Orth and C. M. Duarte (Springer, Dordrecht, 2006), pp. 135–157.
K. J. McGlathery, P. Berg, and R. Marino, “Using porewater profiles to assess nutrient availability in seagrass vegetated carbonate sediments,” Biogeochemistry 56, 239–263 (2001).
K. J. McGlathery, R. Marino, and R. W. Howarth, “Variable rates of phosphate uptake by shallow marine carbonate sediments: mechanisms and ecological significance,” Biogeochemistry 25, 127–146 (1994).
J. Mellors, M. Waycott, and H. Marsh, “Variation in biogeochemical parameters across intertidal seagrass meadows in the central Great Barrier Reef region,” Mar. Pollut. Bull. 51, 335–342 (2005).
M. Nakaoka, and K. Aioi, “Growth of seagrass Halophila ovalis at Dugong trailscompared to existing withinpatch variation in a Thailand intertidal flat,” Mar. Ecol.: Progr. Ser. 184, 97–103 (1999).
E. P. Nobi, E. Dilipan, K. Sivakumar, and T. Thangaradjou, “Distribution and biology of seagrass resources of Lakshadweep group of islands, India,” Ind. J. Geo-Mar. Sci. 40(5), 624–634 (2011).
S. R. Olsen, C. V. Cole, F. S. Watanabe, and L. A. Dean, Estimation of Available Phosphorus in Soils by Extraction with Sodium Bicarbonate. USDA Circular 939 (U.S. Government Printing Office, Washington D.C., 1954).
M. B. K. Prasad, and A. L. Ramanathan, “Sedimentary nutrient dynamics in a tropical estuarine mangrove ecosystem,” Estuarine, Coastal Shelf Sci. 80, 60–66 (2008).
M. B. K. Prasad, A. L. Ramanathan, and T. Dittmar, “Organic matter and mangrove productivity,” in Management and Sustainable Development of Coastal Zone Environments, Ed. by A. Ramanathan, P. Bhattacharya, T. Dittmar, M.B.K. Prasad, and B. Neupane, (Springer Publications, 2010), pp. 175–193.
M. B. K. Prasad and A. L. Ramanathan, “Characterization of phosphorus fractions in sediments of a tropical mangrove ecosystem,” Wetlands Ecol. Manag. 18, 165–175 (2010).
M. B. K. Prasad and A. L. Ramanathan, “Organic matter characterization in a tropical estuarine-mangrove ecosystem of India: preliminary assessment by using stable isotopes and lignin phenols,” Estuarine, Coastal Shelf Sci. 84(4), 617–624 (2009).
M. B. K. Prasad, “Nutrient stoichiometry and eutrophication in Indian mangroves,” Environ. Earth Sci. 67, 293–299 (2012). doi: 10.1007/s12665-011-1508-8.
S. Z. Qasim, P. M. A. Bhattathiri, and C. V. Reddy, “Primary production of an atoll in the Laccadives,” Int. Rev. Gesamten Hydrobiol. 57(2), 207–226 (1972).
K. Ramamurthy, N. P. Balakrishnan, K. Ravikumar, and R. Ganesan, “Seagrass of Coromandel coast of India,” Flora of India-Ser. 4, Botan. Surv. India, (1992).
R. K. Ranjan, J. Routh, A. L. Ramanathan, and J. Val Klump, “Elemental and stable isotope records of organic matter input and its fate in the Pichavaram mangrove-estuarine sediments (Tamilnadu, India),” Mar. Chem. 126, 163–172 (2011).
M. A. Rasheed, K. R. Dew, L. J. McKenzie, R. G. Coles, S. P. Kerville, and S. J. Campbell, “Productivity, carbon assimilation and intra-annual change in tropical reef platform seagrass communities of the Torres Strait, north-eastern Australia,” Cont. Shelf Res. 28, 2292–2303 (2008).
J. Romero, K. S. Lee, M. Pérez, M. A. Mateo, and T. Alcoverro, “Nutrient dynamics in seagrass ecosystems,” in Seagrasses: Biology, Ecology and Conservation, Ed. by A. W. D. Larkum, R. J. Orth and C.M. Duarte (Springer, Dordrecht, 2006), pp. 227–254.
A. Sfriso, and P. F. Ghetti, “Seasonal variation in biomass, morphometric parameters and production of seagrasses in the lagoon of Venice,” Aquat. Bot. 61, 207–223 (1998).
D. Shea, “Developing national sediment quality criteria,” Environ. Sci. Technol. 22, 1256–1261 (1988).
F. T. Short, “Effects of sediment nutrients on seagrasses literature review and mesocosm experiment,” Aquat. Bot. 27, 41–58 (1987).
F. T. Short and C. P. McRoy, “Nitrogen uptake by leaves and roots of the seagrass Zostera marina L.,” Bot. Mar. 27, 547–555 (1984).
F. T. Short and H. A. Neckles, “The effects of global climate change on seagrasses,” Aquat. Bot. 63, 169–196 (1999).
F. T. Short, D. M. Burdick, and J. E. Kaldy, “Mesocosm experiments quantify the effects of eutrophication on eelgrass, Zostera marina,” Limnol. Oceanogr. 40, 740–749 (1995).
F. T. Short and S. Wyllie-Echeveria, “Natural and maninduced disturbance of seagrasses,” Environ. Conserv. 23, 17–27 (1996).
F. T. Short, W. C. Dennison, and D. G. Capone, “Phosphorus limited growth of the tropical seagrass Syringodium filiforme in carbonate sediments,” Mar. Ecol.: Progr. Ser. 62, 169–174 (1990).
R. Sridhar, T. Thangaradjou, and L. Kannan, “Comparative investigation on physic-chemical properties of the coral reef and seagrass ecosystems of the Palk Bay,” Indian J. Mar. Sci. 37(2), 207–213 (2008).
J. D. H. Strickland, and T. R. Parsons, “A practical handbook of seawater analysis,” Bulletin of Fisheries Research Board of Canada, (1972).
J. Terrados, C. M. Duarte, M. D. Fortes, J. Borum, N. S. R. Agawin, S. Bach, U. Thampanya, N. L. Kamp, W. J. Kenworthy, H. O. Geertz and J. Vermaat, “Changes in community structure and biomass of seagrass communities along gradients of siltation in SE Asia,” Estuarine, Coastal Shelf Sci. 46, 757–768 (1998).
Terrados, J. Duarte, C. M. Kamp-Nielsen, L. Agawin, N. S. R. Gacia, E. Lacap, D. Fortes, M.D., J. Borum, M. Lubanski, and T. Greve, “Are seagrass growth and survival affected by reducing conditions in the sediment?” Aquat. Bot. 65, 175–197 (1999).
T. Thangaradjou and L. Kannan, “Marine sediment texture and distribution of seagrasses in the Gulf of Mannar biosphere reserve,” Seaweed Research Utilization 27(1–2), 145–154 (2005).
T. Thangaradjou, K. Sivakumar, E. P. Nobi, and E. Dilipan, “Distribution of seagrasses along the Andaman and Nicobar Island: a post tsunami survey,” in Recent Trends in Biodiversity of Andaman and Nicobar Island, Ramakrishna, Ed. by C. Raghunathan and C. Sivaperuman (Zoological Survey of India, 2010), pp. 157–160.
B. W. Touchette and J. M. Burkholder, “Review of nitrogen and phosphorus metabolism in seagrasses,” J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 250, 133–167 (2000).
J. E. Vermaat, N. S. R. Agawin, C. M. Duarte, M. D. Fortes, N. Marba, and J. S. Uri, “Meadow maintenance, growth and productivity of a mixed Philippine seagrass bed,” Mar. Ecol.: Progr. Ser. 124, 215–225 (1995).
D. I. Walker, and A. J. McComb, “Salinity response of the seagrass Amphibolis antarctica (Labill.) Sonder & Aschers.: an experimental validation of field results,” Aquat. Bot. 36, 359–366 (1990).
M. Waycott, C. M. Duarte, T. J. B. Carruthers, and R. J. Orth, “Accelerating loss of seagrasses across the globe threatens coastal ecosystems,” Proc. National Acad. Sci. 106, 12377–12381 (2009).
C. K. Wentworth, “A scale of grade and class terms for clastic sediments,” J. Geol. 30, 377–392 (1992).
R. C. Zimmerman, R. D. Smith, and R. S. Alberte, “Is growth of eelgrass nitrogen limited? A numerical stimulation of the effects of light and nitrogen on the growth dynamics of Zostera marina,” Mar. Ecol.: Progr. Ser. 41, 167–176 (1987).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
The article is published in the original.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Thangaradjou, T., Bala Krishna Prasad, M., Subhashini, P. et al. Biogeochemical processes in tropical seagrass beds and their role in determining the productivity of the meadows. Geochem. Int. 53, 473–486 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1134/S0016702915050055
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S0016702915050055